Prediction Market Contract
The Prediction Market contract sets up a scenario to determine the outcome of a football game between two teams. The contract uses the Equivalence Principle to ensure accurate and consistent decision-making based on the game's resolution data.
import json
from genvm.base.equivalence_principle import EquivalencePrinciple
from genvm.base.icontract import IContract
class PredictionMarket(IContract):
def __init__(self, game_date: str, team1: str, team2: str):
"""
Initializes a new instance of the prediction market with the specified game date and teams.
Args:
game_date (str): The date of the game in the format 'YYYY-MM-DD'.
team1 (str): The name of the first team.
team2 (str): The name of the second team.
Attributes:
has_resolved (bool): Indicates whether the game's resolution has been processed. Default is False.
game_date (str): The date of the game.
resolution_url (str): The URL to the game's resolution on BBC Sport.
team1 (str): The name of the first team.
team2 (str): The name of the second team.
"""
self.has_resolved = False
self.game_date = game_date
self.resolution_url = 'https://www.bbc.com/sport/football/scores-fixtures/' + game_date
self.team1 = team1
self.team2 = team2
async def resolve(self) -> None:
if self.has_resolved:
return "Already resolved"
final_result = {}
async with EquivalencePrinciple(
result=final_result,
principle="The score and the winner has to be exactly the same",
comparative=True,
) as eq:
web_data = await eq.get_webpage(self.resolution_url)
print(web_data)
task = f"""In the following web page, find the winning team in a matchup between the following teams:
Team 1: {self.team1}
Team 2: {self.team2}
Web page content:
{web_data}
End of web page data.
If it says "Kick off [time]" between the names of the two teams, it means the game hasn't started yet.
If you fail to extract the score, assume the game is not resolved yet.
Respond with the following JSON format:
{{
"score": str, // The score with numbers only, e.g., "1:2", or "-" if the game is not resolved yet
"winner": int, // The number of the winning team, 0 for draw, or -1 if the game is not yet finished
}}
"""
result = await eq.call_llm(task)
print(result)
eq.set(result)
result_json = json.loads(final_result['output'])
if result_json['winner'] > -1:
self.has_resolved = True
self.winner = result_json['winner']
self.score = result_json['score']
return result_jsonYou can check out this code on our GitHub (opens in a new tab)
Deploying the Contract
To deploy the Prediction Market contract, you'll need to initialize the contract state correctly. This will impact how the contract will respond to the game's resolution.
-
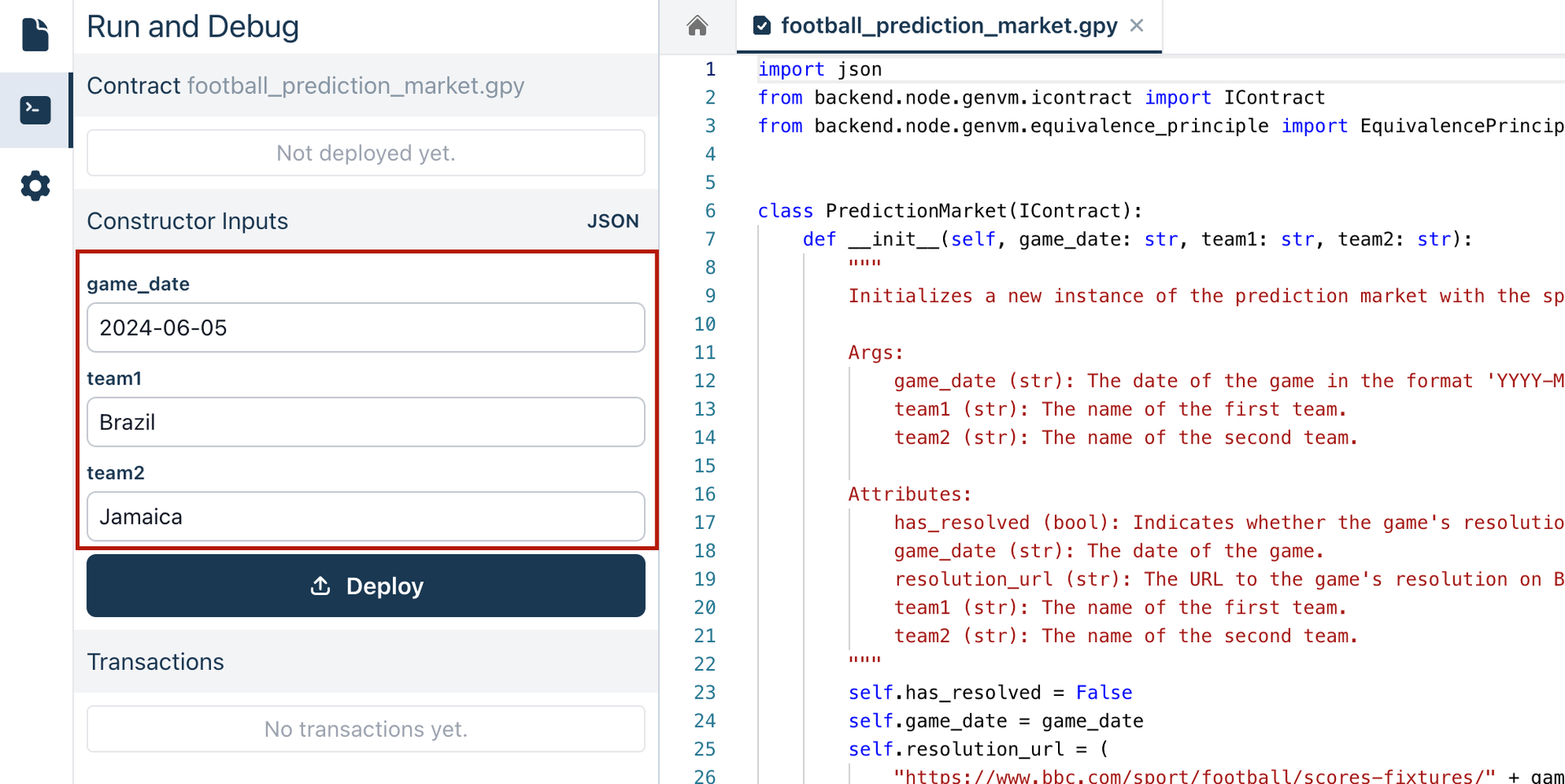
Provide the game date and the names of the two teams. The
game_date,team1, andteam2constructor parameters are automatically detected from the code. For example, you might setgame_dateto "2024-06-05",team1to "Brazil", andteam2to "Jamaica". -
Once the game details are set, deploy the contract to make it ready to interact and resolve the game results.
Checking the Contract State
Once the contract is deployed, its address is displayed as well as the Read Methods section. In this case, there are no Read Methods defined.

Executing Transactions
To interact with the deployed contract, go to the Write Methods section. Here, you can call the resolve method to process the game's result. This triggers the contract's logic to retrieve the game's data and determine the outcome based on the Equivalence Principle criteria defined.

Analyzing the Contract's Decisions
When the resolve method is executed:
- The LLM retrieves the game data from the specified URL.
- It validates the game's outcome according to the Equivalence Principle defined in the code.
- Finally, it returns a JSON response that includes the game's score and the winner.
Handling Different Scenarios
- If the game has started but not finished, the JSON response will indicate the game is not resolved yet.
- If the game has finished, the JSON response will include the final score and the winning team.
- If the game hasn't started, the JSON response will indicate this status.
You can view the logs to see detailed information about the contract interaction.